- In this header bidding guide, we will explore the basics of header bidding, including how it works, its benefits, and the technology required to implement it.
- Also read about the different types of header bidding and its alternatives by different companies.
Header bidding is a programmatic advertising technique that has revolutionized the way publishers monetize their website's ad inventory. Whether you're a publisher looking to increase your ad revenue or an advertiser seeking to improve the effectiveness of your ad campaigns, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and insights you need to get started with header bidding.
What is header bidding
Header bidding is an advanced programmatic approach where publishers make their inventory available to multiple ad networks and ad exchanges at the same time. This enables them to set the maximum price for the inventory, therefore, boosting ad revenue.
In other words, bid requests are sent to multiple demand partners simultaneously in real time, thereby maximizing the inventory value by enabling each ad impression to be sold at the maximum price. The demand partner with the highest bid wins the programmatic auction and gets to advertise on the publisher’s inventory. The entire process takes only a fraction of a second.
According to a Statista report, 70% website publishers and 16% of the the top 100,000 website publishers used header bidding in Q2 of 2022. More than half of the US publishers claimed to achieve a higher yield through header bidding implementation.
Elevate Your Ad Earnings - Get Started with Mediation!
What was before header bidding
Before header bidding, a publisher’s inventory was sold in a sequential manner. The direct demand partners would sit in the order of priority and get a chance to bid first based on the frequency capping. When the direct order and frequency capping was exhausted, the inventory would be sold using the waterfall approach, where advertisers would bid on the ad impression one by one.
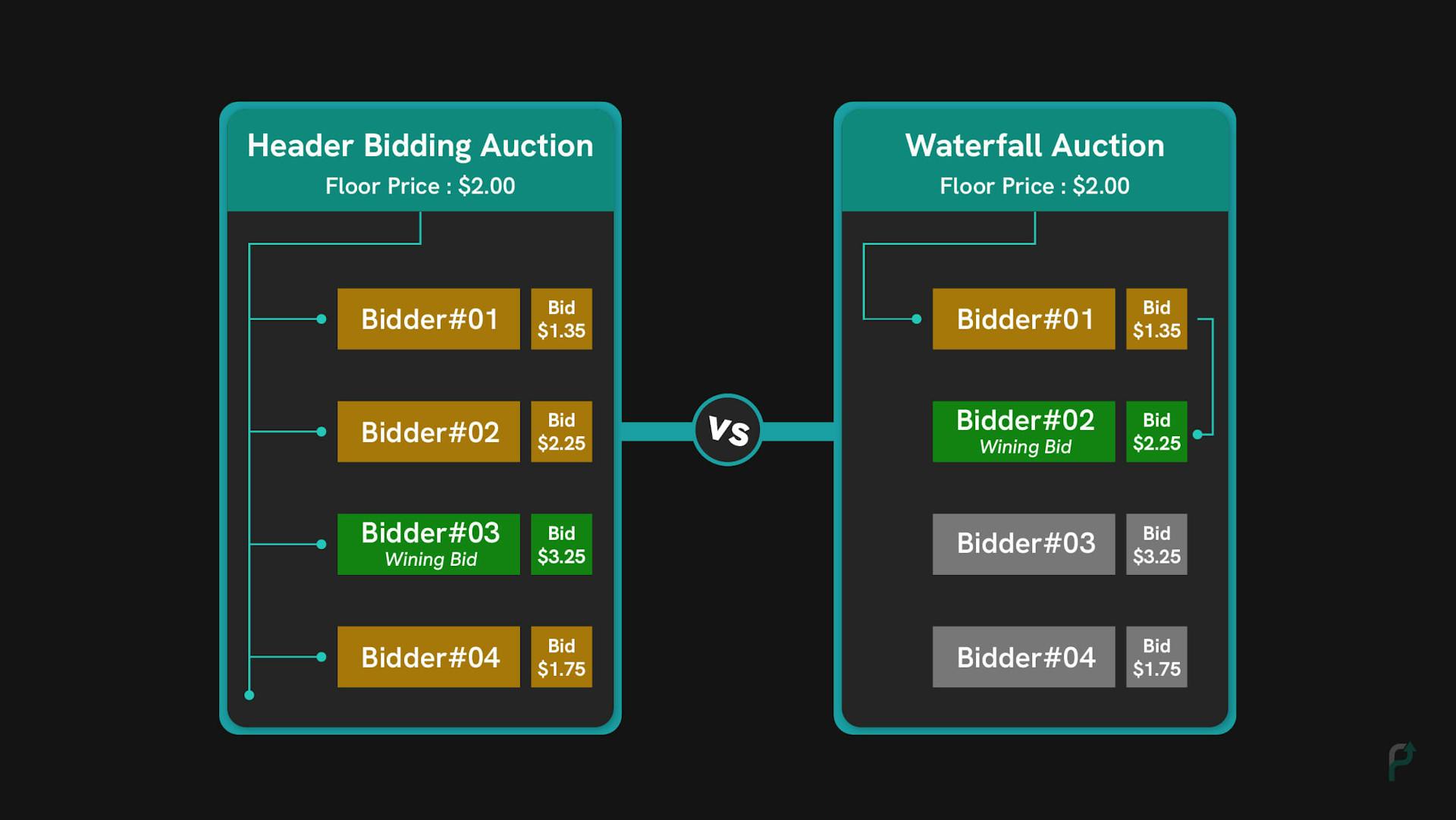 Header Bidding vs Waterfall Bidding
Header Bidding vs Waterfall BiddingThe main drawback of the waterfall system was that it did not guarantee the maximum price for the inventory. For instance, if bidder 1 bid for $0.2, bidder 2 bid for $0.3, the inventory would be sold to bidder 2, even though bidder 3 was ready to pay $0.35.
Types of header bidding: Client-side vs. server-side
Header bidding starts right when the web page starts to load on a user’s browser. Soon the header bidding wrapper initiates an auction by sending bid requests to all the bidding partners.
The header auction follows the first-price auction setup, where the highest bidder wins the auction and gets to advertise on the publisher’s inventory.
However, before the header auction starts, the bid requests are sent to the wrapper, and the wrapper decides which demand partners will participate in the header auction. In such an auction, if no demand partners are selected, then the backup networks like AdSense take over the auction and the inventory is offered to them on the basis of the Ad Manager settings.
This entire header bidding can take place in two ways: Client-side and server-side.
- In client-side header bidding, the header auction takes place on the user’s browser, where cookie matching is used for better targeting and allowing advertisers access to bid-level data. The problem with this approach is that the page latency is affected. Since the auction happens on the browser, the page loading time may increase.
- In server-side header bidding, the header auction takes place on the publisher’s ad server. Browser resources and network bandwidth are not used in this case, thus not affecting the page latency. However, because cookie matching is not used, targeting as accurate as client-side header bidding cannot be expected.
To overcome the limitations of client-side and server-side bidding, a third type – hybrid header bidding is used. In this case, auctions are held on both the user’s browser and the publisher’s ad server, and the winning bid is picked from the two.
This technique takes advantage of the upsides of both client and server-side header bidding. So, cookie matching is leveraged while maintaining the page latency.
How does header bidding work
Publishers integrate a JavaScript snippet (wrapper) into their website code’s <head> section to generate bid requests through the web browser. The publisher’s ad server filters these bids and then shows the highest bidder’s ad on the ad space.
The process starts as soon as the page loads on a web browser. Below are the steps that take place in the header bidding setup.
- A user visits a website that has ad space available.
- The code sends a request to multiple ad exchanges, asking for bids on the available ad space. These ad exchanges can include Google AdExchange, AppNexus, Rubicon Project, etc.
- Demand partners who are interested in displaying their ads on the website respond with bids in real-time.
- The bids are then collected and sent to the website's ad server.
- The ad server uses the information provided by the bids to determine which ad to display.
- The ad is then loaded onto the website and the impression is recorded.
Publishers can control which advertisers can bid on their inventory and even increase the price of their premium inventory. The entire benefit of header bidding lies in the fact that the publisher does not depend on a single supply side platform to get demand.
Thus, overall fill rate and yield increase for the publisher. Additionally, there is a decrease in reporting errors as only a single auction is held instead of sequential bidding.
Why should publishers choose header bidding
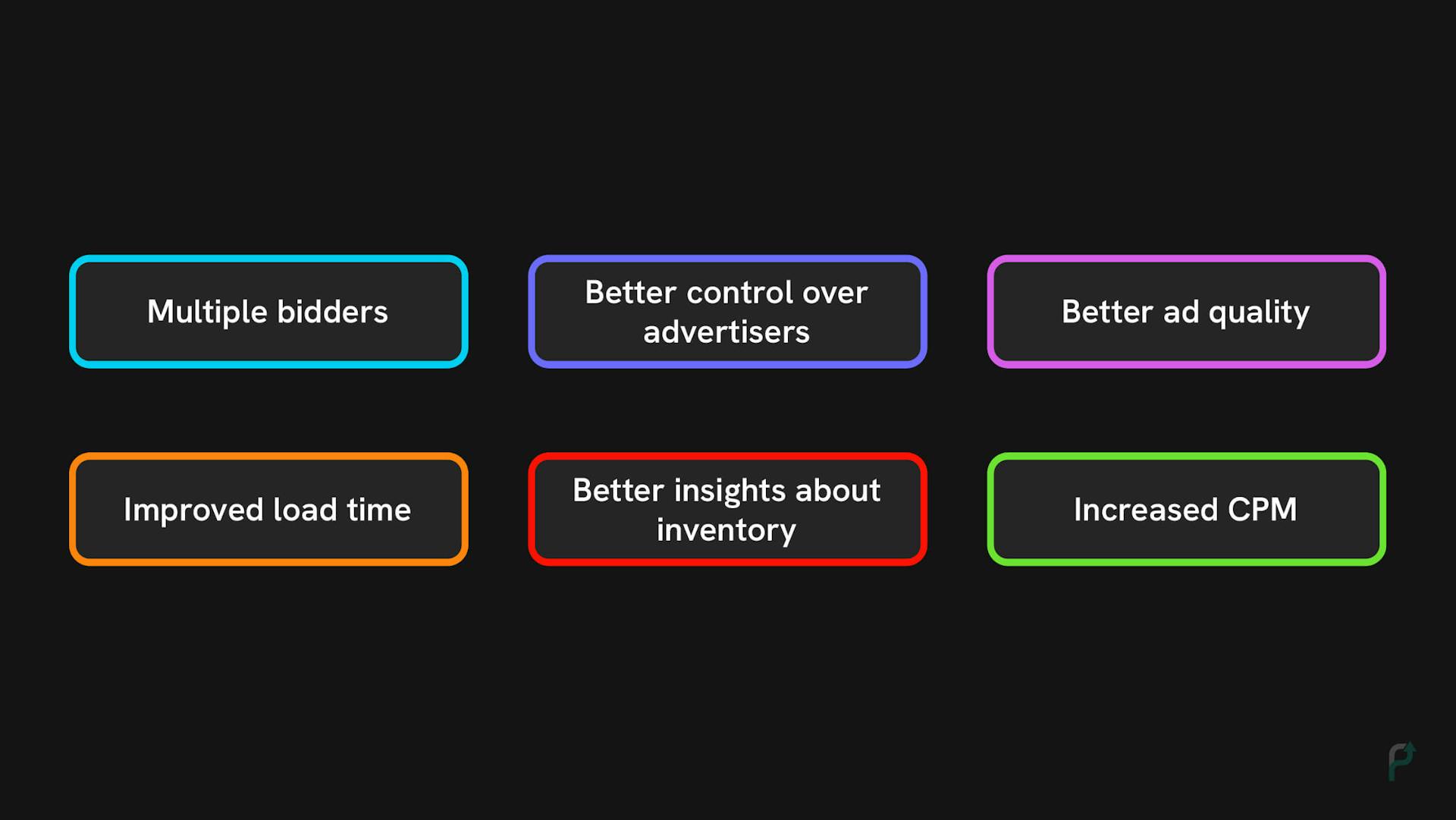 Benefits of Header Bidding
Benefits of Header BiddingNo reliance on a single SSP allows publishers to increase yield through better allocation of ad impressions and improved fill rates. Below are some benefits of header bidding for publishers.
- Multiple bidders: Since the auction happens simultaneously between multiple ad networks and exchanges, multiple demand partners bid for the inventory.
- Better control over advertisers: Publishers can control which demand partners can bid for their inventory. They can even prevent certain advertisers from bidding and even prioritize some advertisers over the others.
- Better ad quality: Since publishers can choose certain advertisers to bid on priority, they may expect higher bid prices. This increases competition among all the bidders, improving the chances of getting better ads.
- Improved load time: With server-side header bidding, the time taken to choose the winning bid and display an ad is less. This improves the website’s user experience and SEO results.
- Better insights about inventory: When the inventory is sold for a higher price than the floor price because of increased competition between advertisers, publishers get insights into the real value of their inventory.
- Increased CPM: With advertisers competing for the premium inventory, better CPM is guaranteed. Thus, the ultimate goal of increasing the website’s ad revenue is achieved.
Smart Choices, Bigger Profits: Ad Mediation Solutions Tailored for Publishers!
How is header bidding beneficial to advertisers
In addition to providing publishers with several benefits, header bidding has also proven to be advantageous to advertisers in many ways.
- Access to premium inventory: Since publishers can prioritize advertisers and demand partners, it gives advertisers access to premium publisher inventory that would rather be available through direct deals in a non-header bidding setup.
- Reduced intermediaries: No matter what ad exchanges are used, all advertisers get equal access to the best publisher inventory available.
- Transparency in process: The entire process of header bidding is transparent owing to reduced intermediate parties. Moreover, the reporting is transparent, giving advertisers access to accurate information.
How to setup header bidding
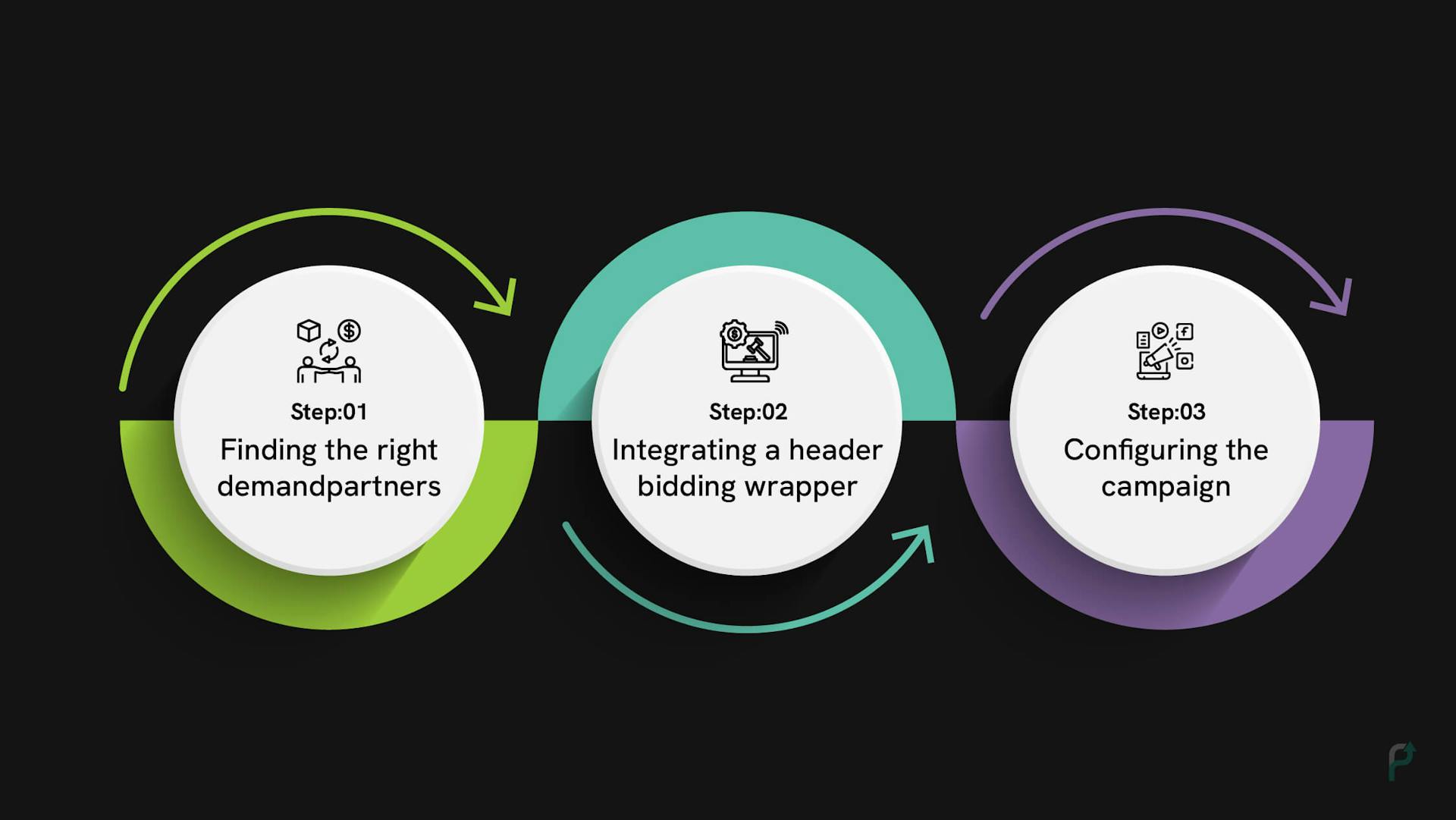 Header Bidding Setting-up Steps
Header Bidding Setting-up StepsAlthough setting up header bidding may require technical expertise, here are three simple steps to successfully configure it on a website.
Step 1: Finding the right demand partners.
After building a good website or app that meets all the monetization standards, publishers must target demand partners that match the website’s niche. When the target audience for the ads is right, the better the impressions, clicks, views, etc., on the ads will be, thereby increasing ad revenue. More factors must be considered than just the demand partner’s reputation.
Step 2: Integrating a header bidding wrapper.
Header bidding wrappers are like a repository for demand partner code. They help in organizing the auction and set up the rules for the same.
Step 3: Configuring the campaign.
The last step is to set up the configurations for ad campaigns. Specify the timelines for auction termination, set up floor pricing, create ad units, and specify any other limitations as needed.
What are header bidding wrappers
Publishers need to send bid requests each time an ad impression is available. For each bidding partner that joins the auction, their code snippet needs to be added to the website. Making changes to the code by adding or deleting bidding partners’ code may become tedious for publishers.
Therefore, the header bidding wrapper manages the entire auction by acting as a container for all the bidding partner codes.
Furthermore, some wrappers provide a GUI from which bidding partners can be added or removed from the auction through a simple toggle, eliminating the need for modifying the code.
Also, the analytics tools that come with the header bidding can be used to determine the performance of the demand partners participating in the bidding process.
To summarize, there two main responsibilities of header bidding wrappers:
- To run header auctions by sending bid requests to bidding partners and getting their bids.
- To set up rules to ensure efficient and systematic auctions. The rules are to decide when the auction starts, how many bidding partners participate, how long the auction waits to receive bids (timeout), what the floor price is, and more.
Some popular examples of header bidding wrappers are Pubfood.js, BiddR 360, and Predbid.js.
What is Predbid.js
Prebid.js is the most popular and extensively used open-source header bidding wrapper. Publishers can use this free JavaScript library to implement header bidding on their websites. Prebid.js is supported by lots of ad partners and vendors. It offers publishers a selection of ready-made adapters for various ad networks as well as an adaptable API that can be used to interface with unique bidders.
Advantages and disadvantages of Prebid.js
Advantages
- Effective ad server communication tools
- Increased speed with header auctions compared to waterfall
- Large user community which contributes to upgrades and operational support
- Open-source and free to use
Disadvantages
- Complex to set up, not user-friendly
- Publishers may have to pay for the integration of vendors, support, and other services
- Technical expertise is required for implementation
- Support is not on-demand or paid
What are header bidding adapters
Header bidding adapters are software that enable publishers to connect their ad inventory with demand sources.
When a user visits a website, the header bidding adapter sends a request to all the demand partners simultaneously, inviting them to participate in the auction. The demand partners then respond with their bids and the highest bidder wins the auction, and their ad is displayed on the website.
Header bidding adapters are used by publishers to improve the competition for their inventory and increase their ad revenue.
Advertisers also benefit from header bidding since it gives them access to a broader range of inventory, making it more likely to find the right audience for their ads.
Difference between wrappers and adapters
| Wrapper | Adapter |
|---|---|
| A header bidding wrapper is a piece of code that publishers use to manage multiple header bidding partners in a unified manner. | A header bidding adapter is a piece of code that connects the demand partner's technology to the header bidding wrapper. |
| The wrapper is responsible for conducting the auction process by sending bid requests to all the demand partners simultaneously and collecting their bids. | It enables the demand partner to receive bid requests from the wrapper, respond with a bid, and receive the winning bid notification. |
| The wrapper then selects the highest bid and sends it back to the website's ad server to be displayed. | Each demand partner typically requires its own adapter to integrate with the header bidding wrapper. |
What is mobile header bidding
It is similar to traditional header bidding, which was introduced to desktop advertising, but has been adapted for mobile devices.
With mobile header bidding, publishers can increase the competition for their ad inventory and potentially increase revenue by allowing multiple demand sources to bid on the same ad impressions in real-time. This results in more efficient and effective auctions and can lead to better ad targeting and user experience.
In mobile header bidding, the auction takes place in the header of the mobile web page or app before the page or app loads. The process starts when the user requests a page or app to load, and the mobile header bidding technology sends a request to all the demand sources, asking them to bid on the available inventory. The highest bidder wins the auction and their ad is served in the mobile app or webpage.
Prebid SDK
The Prebid SDK is an open-source solution that allows publishers to integrate with a variety of demand partners and ad networks. It supports both server-side and client-side header bidding, providing publishers with more flexibility and control over their ad inventory.
The SDK includes features such as support for multiple ad formats, advanced targeting capabilities, and real-time reporting and analytics. It also includes a range of integrations with popular ad servers and ad mediation platforms, making it easy for publishers to get started with header bidding.
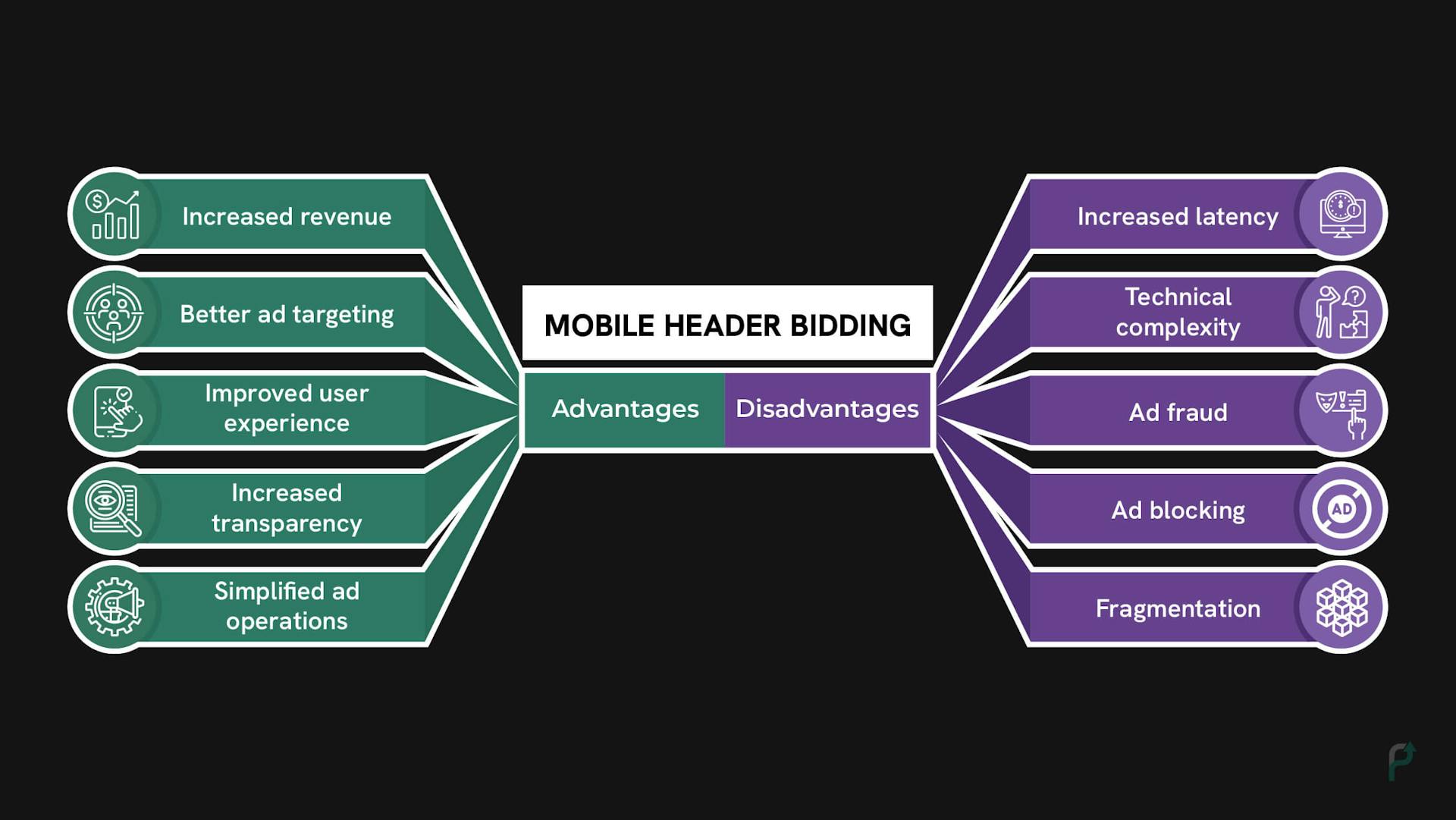
Benefits of mobile header bidding
- Increased revenue: Mobile header bidding allows publishers to sell their ad inventory to the highest bidder, which can result in increased revenue compared to traditional waterfall ad serving.
- Better ad targeting: By allowing multiple demand sources to bid on the same ad inventory, mobile header bidding increases competition and can result in more targeted and relevant ads for users.
- Improved user experience: With mobile header bidding, ads load faster and more efficiently, which can lead to a better user experience and increased engagement.
- Increased transparency: Mobile header bidding offers more transparency into the auction process, allowing publishers and advertisers to see who is bidding on their inventory and at what price.
- Simplified ad operations: Mobile header bidding reduces the need for complex ad operations and eliminates the need for manual ad server adjustments, which can save time and resources for publishers.
Maximize ad revenue, minimize effort – choose mediation for apps.
Disadvantages of mobile header bidding
- Increased latency: Mobile header bidding can increase the latency of the ad serving process, as the auction takes place before the page or app loads. This can result in slower load times and potentially impact user experience.
- Technical complexity: Mobile header bidding requires technical expertise and resources to implement and maintain, which may be a barrier for smaller publishers.
- Ad fraud: With multiple demand sources bidding on the same ad inventory, there is a greater risk of ad fraud and invalid traffic.
- Ad blocking: Some users may choose to block ads, which can reduce the demand for ad inventory and decrease revenue for publishers.
- Fragmentation: With multiple ad exchanges and demand sources involved in the bidding process, there can be fragmentation in the auction process, which can make it difficult for publishers to optimize their ad inventory.
 Advantages and disadvantages of Mobile Header Bidding
Advantages and disadvantages of Mobile Header BiddingWhat is video header bidding
Video header bidding is a programmatic advertising technique that allows publishers to offer video ad inventory to multiple demand sources simultaneously, increasing competition and potentially resulting in higher ad revenue. It works similarly to traditional header bidding, but is specific to video advertising.
In video header bidding, the publisher's video player sends a request for bids to multiple ad exchanges or demand-side platforms (DSPs) simultaneously. The exchanges or DSPs respond with bids, and the highest bidder is selected to serve the ad. The winning bid is then sent to the publisher's ad server, which delivers the ad to the video player.
Benefits of video header bidding
- It allows publishers to maximize the value of their ad inventory by increasing competition among demand sources.
- It also provides more transparency and control over the ad serving process, allowing publishers to set their own floor prices and manage their relationships with demand sources.
Disadvantages of video header bidding
- Video header bidding can be complex to set up and requires specialized technology, such as a video header bidding wrapper, to facilitate the bidding process.
- It also requires a fast and reliable internet connection to ensure that the bidding and ad delivery processes occur in real-time, without affecting the user experience.
What is open bidding by Google
Header bidding was not introduced by a single person. Instead, it is the result of the frustration of publishers with the inefficiencies of the waterfall model. It also competed with Google AdX in real-time bidding.
Google released open bidding, earlier known as Exchange Bidding or Exchange Bidding in Dynamic Allocation (EBDA), a server-side alternative to header bidding.
Server-side means that the auction takes place on the ad server instead of the web browser. With exchange bidding’s server-to-server auctions, publishers can bring their own demand as well as get access to Google AdX demand. Demand partners from both parties compete against each other to win the publisher’s ad inventory.
Open bidding (EBDA) vs. header bidding
Although both open bidding and header bidding are meant to show the right ads to the right users and the right time, it completely depends on the publisher to choose on setup depending on their requirements and technical expertise.
EBDA offers a wholesome reporting system, detailed billing information, and transparency through the Exchange Bidding Data Transfer File. It even reduced the complexity of implementation. On the other hand, header bidding also offers transparency and an efficient approach to maximize yield.
A hybrid system which is a mix of both can be used for the best results.
Why is it better than AdSense
Although AdSense is a well-known ad network, header bidding is preferable in a number of respects, including the ability to add or delete demand partners. Due to the rise in the interest of large advertisers in header bidding inventory, header bidding is recognised to give better eCPM than AdSense.
Advertisers chose header bidding because it was transparent and there was fair competition, which increased the flow of advertising dollars through private marketplaces or PMPs.
Header bidding on AMP
It’s a given that monetizing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is not an easy task. This is because AMP uses its own library files rather than allowing third-party JS tags on the pages. Amp-script allows for the addition of custom JavaScript tags. However, your code will be subject to certain limitations and will run in a Web Worker.
You can implement header bidding on AMP through Real-Time Configuration (RTC) and a header bidding wrapper, as RTC supports only up to five demand partners. Server-side header bidding can be implemented through this setup. Let’s see how it works.
How does RTC work with a wrapper
RTC allows ad servers to dynamically adjust the price and targeting of ad inventory in real-time, based on factors such as user behavior, ad performance, and market conditions. This can help to increase revenue for publishers and improve the effectiveness of ad campaigns for advertisers.
Header bidding wrapper, on the other hand, is a technique used to facilitate header bidding, which is a process where multiple ad exchanges are given an opportunity to bid on ad inventory simultaneously. This can help to increase competition among ad exchanges and improve the prices that publishers receive for their ad inventory.
When used together, RTC and header bidding wrapper can help to optimize programmatic advertising by allowing ad servers to dynamically adjust the prices and targeting of ad inventory in real-time, based on the bids received from multiple ad exchanges.
For example, when a user visits a website, the header bidding wrapper sends bid requests to multiple ad exchanges simultaneously. The ad exchanges respond with bids, and the wrapper sends the bids to the ad server, which uses RTC to dynamically adjust the prices and targeting of the ad inventory based on the bids received.
Overall, combining RTC and header bidding wrapper can help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of programmatic advertising, providing benefits for both publishers and advertisers.
Amazon’s header bidding solution: UAM and TAM
Amazon Publisher Services or APS offers two header bidding alternatives.
- UAM (Unified Ad Marketplace): The Unified Ad Marketplace (UAM) by Amazon is a server-side header bidding wrapper. The header bidding auctions are conducted on Amazon's servers rather than within consumers' browsers.
- TAM (Transparent Ad Marketplace): For enterprise publishers with large exchanges, Transparent Ad Marketplace (TAM) is Amazon's server-side header bidding solution. It works on an invitation-only basis. Publishers who use TAM are required to have direct agreements with SSPs like Amazon and manage them independently. The payments are also handled separately for each bidder. Also, publishers need a formal contract with any demand partners they desire to collaborate with.
Benefits and drawbacks of UAM
Benefits
- Managed service: As creating a header bidding wrapper takes time and resources, using a managed wrapper is more efficient.
- Page latency: Compared to client-side header bidding, employing a server-side header bidding solution has a comparatively modest impact on page latency because the auctions are done outside of the users' browsers.
- Increased demand: With an ad tech partner that gives access to many SSPs, including Amazon, publishers can grow demand and increase their revenue potential.
- Timely and single payouts: Amazon pays publishers a single payment on a Net-60 basis after combining the earnings from each activated SSP (together with their bidders).
- Interoperability with the existing HB configuration: The integration of UAM header bidding does not interfere with the publisher's present header bidding setup. The integration also boosts publishers' earnings.
- Increased revenue: To enhance yield at the impression level, additional bids will first compete for your ad impressions. In order to compete, it also motivates demand partners to raise their offers.
Drawbacks
- Basic reporting: UAM offers basic filtering options as well as information for reporting, including bid requests, impressions, and income. However the level of depth and granularity in these data is lacking.
- Complex setup: It takes a lot of effort to run server-side wrappers concurrently. Concurrently. A lot of time is required to set them up and constant checking is needed to ensure that everything is going right.
- No transparency: There is restricted access to Amazon’s auction mechanism and bid-level data.
Benefits and drawbacks of TAM
Benefits
- No costs: There are no costs associated with TAM for enterprise publishers.
- More demand: Publishers get access to Amazon's demand in addition to their current SSP partners.
- Transparent reporting: TAM users who choose auction-level reporting get access to more information about the bidders and winners.
- Control: TAM implementation offers more control as publishers are the sole owners of all the SSP contracts, including the setup.
Drawbacks
- Multiple payments: You receive payments from each SSP in accordance with your agreements instead of a single payment from Amazon.
- Difficult execution: A new server-side header bidding wrapper requires extensive technical management, which requires both resources and experience.
- Contracts for more demand: You must have contractual agreements with SSPs to get demand from them through TAM.
Disadvantages of header bidding
- Page latency: In the case of client-side header bidding, the auctions take place on the user’s browser, negatively impacting the page latency.
- Complex setup: The header bidding setup is complicated as it involves choosing a wrapper, modifying the demand partner code, and other complex tasks.
- Higher cost: The cost of running header auctions is higher as it requires dedicated human resources to manage the bidding process and oversee the performance.
- Technical expertise: Implementing the header bidding code and modifying demand partner code may need dedicated expertise.
- Lack of transparency: In server-side auction, publishers get limited information about bid-level data and demand partner performance. Hence, there is not enough room for improvement.
- Browser compatibility: To achieve the best performance, client-side header bidding must be backward compatible with browsers. It must even be compatible with all the browsers and their behaviors.
- Duplicate bids: If multiple header bidding partners are used, there is a risk of putting the same impressions for sale. This drawback exists in both client-side and server-side header bidding.
List of 10 best header bidding companies
-
Prebid.js:
Prebid.js is an open-source header bidding solution widely used in the industry. It allows publishers to integrate with multiple demand partners and manage their header bidding setups efficiently.
-
Index Exchange:
Index Exchange is a global advertising marketplace that provides a header bidding solution. It offers a transparent and fair marketplace for both publishers and advertisers.
-
AppNexus (now part of Xandr):
AppNexus, now part of Xandr, is known for its comprehensive ad tech platform. It offers a header bidding solution that enables publishers to optimize and maximize their ad revenue.
-
Rubicon Project:
Rubicon Project is an independent advertising exchange that provides a header bidding solution. It aims to facilitate efficient and fair transactions between buyers and sellers.
-
OpenX:
OpenX is an advertising technology company that offers a header bidding solution for publishers. It focuses on maximizing the value of each impression for both publishers and advertisers.
-
PubMatic:
PubMatic is a digital advertising technology company that provides a comprehensive platform, including a header bidding solution. It aims to automate and optimize the ad buying and selling process.
-
Sovrn:
Sovrn is an advertising technology company that offers various solutions, including header bidding, to help publishers optimize their ad inventory and increase revenue.
-
Criteo:
Criteo is known for its performance marketing solutions, including a header bidding solution. It focuses on delivering personalized and relevant ads to users.
-
TripleLift:
TripleLift is an advertising technology company specializing in native advertising. It offers a header bidding solution to enhance the efficiency of programmatic advertising.
-
District M:
District M is an advertising exchange that provides a header bidding solution. It focuses on creating a transparent and efficient marketplace for publishers and advertisers.
Hope this guide answered all your questions about header bidding. If you have more queries, feel free to reach out to us and we’ll resolve them for you!
Also, don’t forget to share this abundance of information with your fellow publishers who are considering header bidding.
Frequently Asked Questions
The only ad platform built for developers by developers.
Contact us now for a product that fits your needs! It’s quick, simple and easy.



